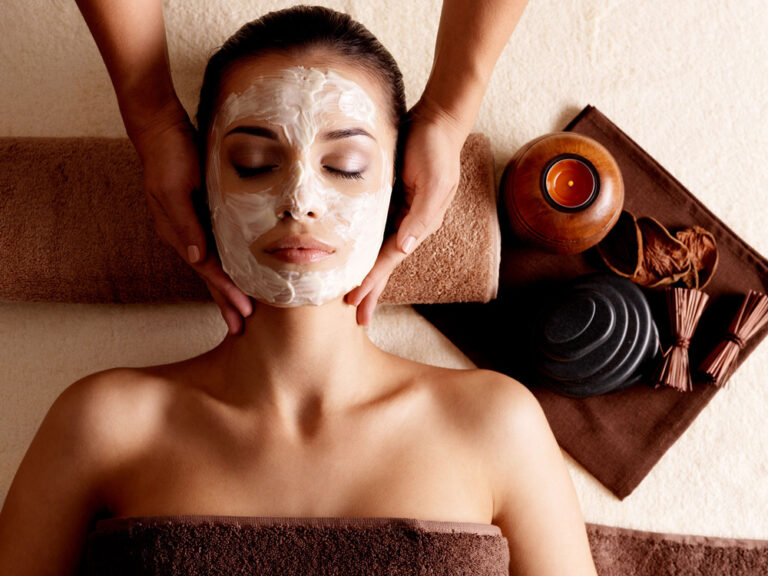
When it comes to achieving silky-smooth skin, waxing and sugaring are two of the most effective hair removal techniques available.…
Cleanfit Reinigung – Your Trusted Cleaning Partner in Zürich
Finding a reliable and professional cleaning service in Zürich can be challenging. Whether you need a thorough umzugsreinigung zürich, an…
Selected Lines: Elevating Modest Fashion with Elegance
In the world of fashion, where trends come and go, elegance remains timeless. Selected Lines, a premier fashion brand based…
Transform Your Health with Claire Almaer—Expert Nutritional Therapy in Liège
What if you could feel more energized, confident, and healthy—all through the power of nutrition? Meet Claire Almaer, a certified…
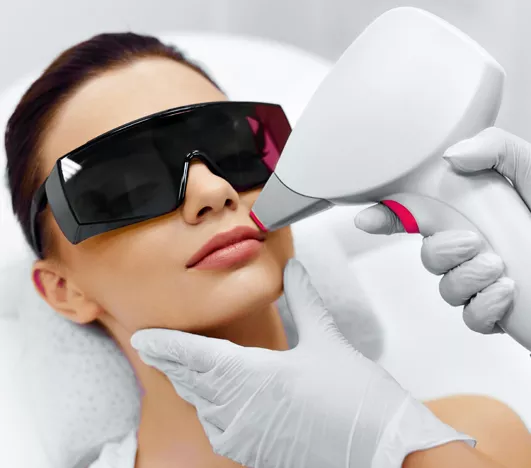
How Laser Haarentfernung Transforms Your Beauty Routine
Maintaining smooth skin shouldn’t be a constant struggle. With laser haarentfernung at Veyu, you can simplify your beauty routine and…
iGamingScan – Your Ultimate Guide to the Best Online Casinos
The online casino industry is more competitive than ever, with new platforms emerging daily. Whether you’re a player looking for…
HonestSMM – The Ultimate SMM Panel for Social Media Growth
In today’s digital landscape, social media presence is everything. Whether you’re an influencer, brand, or entrepreneur, your success depends on…
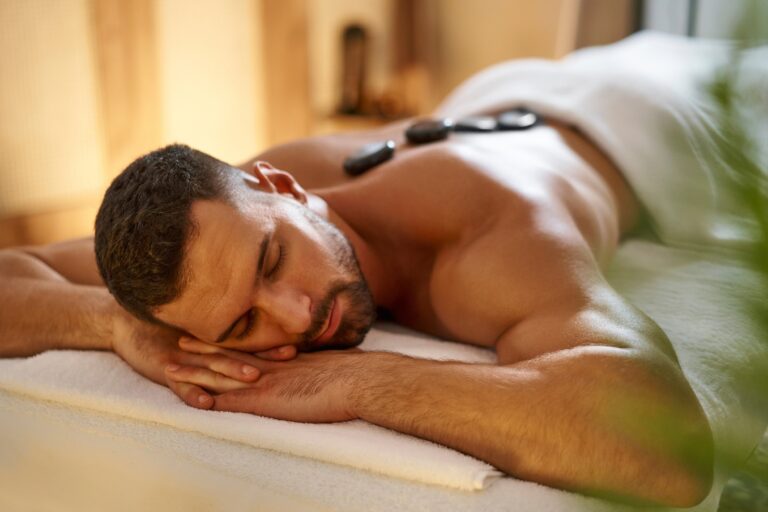
“Escape the Ordinary: Indulge in the Best Body Massage in Dubai”
In a city known for its extravagance, your relaxation should be no exception. At 5 Star Luxury Spa, we offer…
Discover Unbeatable Savings at The Ultimate Online Deals
In today’s fast-paced world, finding quality products at affordable prices can be a challenge. Enter The Ultimate Online Deals, your…
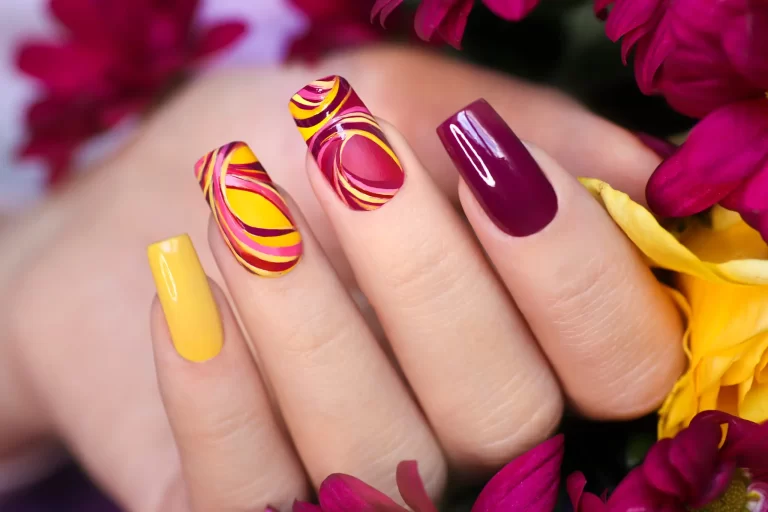
Kanail Spa: The Premier Nail Salon Near You in Langley
Are you on the lookout for a luxurious nail salon near you? Look no further than Kanail Spa, the go-to…